How to prevent misinformation
Help your child spot misleading information online
Get practical tips to help your child develop the skills they need to spot misinformation and make informed choices about sharing content with others.
 Close video
Close video
Quick tips
4 tips to help kids think critically about information
With the growth of social media platforms, online games and instant messaging apps, children are able to talk to anyone – friends or strangers – from around the world within minutes. This can benefit many by making them feel less isolated but for some, it can leave them vulnerable to grooming.
From our research, we know that online ‘stranger danger’ is a concern, particularly for younger children. The key thing to remember is that equipping children with the right advice to make smarter choices online can minimise the risks of exposure to online grooming.
The best way to deal with grooming is to prevent it from happening by making sure your child is well-informed, uses privacy settings on social media sites and knows that they can talk to you if they feel unsafe or worried. Teach your children how to stay safe online:
What does misinformation look like?
Like any online safety issue, regular conversations about misinformation can help children approach things with a critical eye.
Talk about what it looks like and the harm it can cause. You can even use news stories or real social media posts to talk about whether it’s trustworthy and how they know.
Spend time together looking at the privacy settings that can benefit their online safety. It’s always best to assume that default settings are public and should be changed accordingly. We’ve got some advice on using privacy settings on the most popular social apps.
How do you know if something is fake?
Discuss with your child the common things that show something isn’t true. However, remind them that even if something looks legitimate, they should still check it’s trustworthiness.
Common signs something might be false include:
- Grammar or spelling that is incorrect or confusing;
- Emails or messages from unknown sources;
- Cheap or discounted items that are usually expensive;
- Big claims that something is a ‘miracle’ or ‘unbelievable’;
- The information could harm some people.
Above all else, if you feel like something is too good to be true or is ‘off’, check it. It’s better not to share something than to spread misinformation.
How can you check that something is true?
Discuss with children the ways they can check that something is true. Maybe that means they need to find 2 more sources that confirm the information. Or, maybe they need to use fact-checking tools before sharing something.
Popular fact-checking tools include:
Help children stop the spread of misinformation
Teach children these 3 steps to stopping the spread of misinformation.
- Wait: If something seems too good to be true, wait. Instead of sharing things immediately, take a few days to let it sit. See how other people react to it and whether it seems factual.
- Read it: Encourage children to read the whole article or watch the whole video instead of just the title. Often, misinformation can spread by people only reading the main headline instead of learning the whole story.
- Check it: Show children how to fact-check to make sure the information they share is real and truthful.
More on the page
- Why it’s important to prevent misinformation
- How to help children spot false information
- How to stop the spread of misinformation
- Featured misinformation articles
Why it’s important to prevent misinformation
Spreading false information can cause harm in different ways. So, it’s important to make children aware early.
Making sure that children have access to reliable information can help provide them a balanced view of the world around them. It also helps them stay informed, therefore protecting them from scams and hoaxes.
Furthermore, some misinformation is incredibly harmful. It might encourage people to take harmful medications or avoid official guidance from educated people. This could lead to health problems, illness and further physical harm.
How to help children spot false information
Help children and young people develop their media literacy with these tips to spot false information. Knowing what to look for will help protect them from potential harms.
How to spot fake images
Fake images are nothing new. But with the reach of the internet, fake images can spread a lot further and fool a lot more people. Additionally, the popularity of generative artificial intelligence like ChatGPT means there’s an increased risk of fake images spreading.
Still, there are ways to fact check images to help stop the spread of misinformation.
Use Google Lens
Children can use Google Lens on their device to check the source. Within the Google website, they can click the camera icon to upload an image and search that way. You can access it this way on Apple devices.
Android devices have the option to search via Google Lens embedded when you use Google Photos.
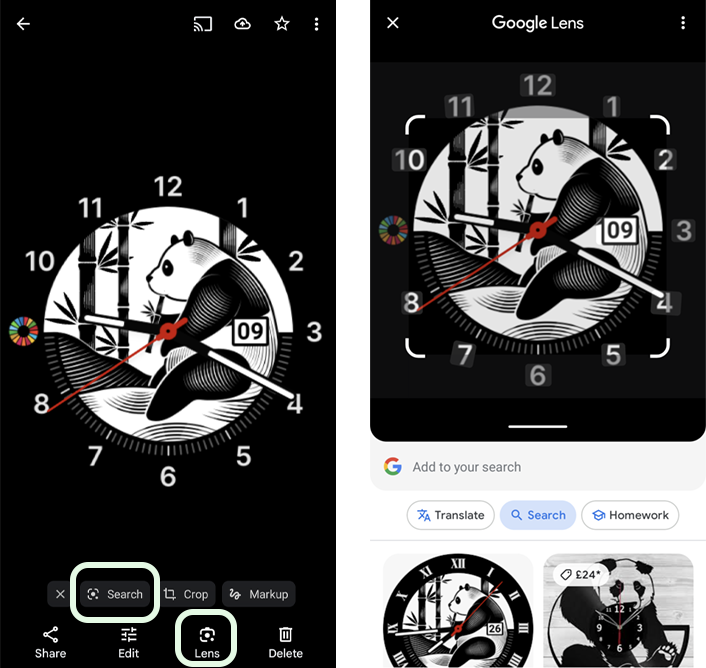
When you search an image, Google can find similar images and the websites they come from. You can then check the whether the sources are trustworthy. Misinformation can spread from untrustworthy sites as well as from incorrect context.
How to spot fake videos
Checking whether a video is real is often more difficult than images. This is because there isn’t a simple reverse search or free software like Google Lens.
Source: BBC
 Close video
Close video
Additionally, while some videos use classic editing techniques that make it easy to identify, some don’t. Cheapfakes refer to false videos that use noticeable editing techniques like changing the speed or colour, or using voiceovers and cutting scenes.
Deepfakes, on the other hand, manipulate an existing video in less detectable ways through artificial intelligence. So, how do you fact check videos?
Look for anything unnatural
It’s hard to detect good deepfakes. One thing to look for, though, is strange or unnatural movements. Maybe the person blinks strangely, or perhaps their words don’t match their mouth movement. They might even move in sudden or unnatural ways.
These things are often very subtle, so you must look closely and possibly watch the video multiple times.
Listen to how people speak
If the video features a speaker, listen to the audio. Does it sound like it’s slowed down or sped up? Are there any points where the audio cuts in a strange way?
Speeding up or slowing down videos, even a little bit, affects the image as well. If the person is moving quickly or slowly, it might be a sign of editing.
Check the background
A deepfake might feature someone in a place they haven’t been. So, signs of this could include a mismatch between the background and the person. Again, look closely as this might happen in one instant but be easily missed elsewhere.
How to stop the spread of misinformation
Helping children develop key media literacy and critical thinking skills can help stop the spread of misinformation.
Read it, check it and wait
Regardless of your child’s skill or ability, this phrase can help them think about what they share with others online.
Read it
- Teach your child to read the whole of whatever they see before sharing it. So, if it’s an article, that means reading the whole article and not just the headline. If it’s a video, it means watching the whole video and not just reading the title
- Clickbait titles often mislead people with outrageous statements so that people click through. As such, reading the whole article (if it’s from a safe source) is important
Check it
- Encourage children to find multiple sources for the information they find online before sharing it. For example, you might require them to find 2 more websites saying the same thing before sharing. Or, you might show them how to look up information on Full Fact or BBC Verify first
Here are some questions children and young people can ask themselves to determine if something is real or fake:
- Who wrote it? You can check the author on the page or go to the about us or contact pages to see who is the person or the organisation that have a Google search to see what else you can learn about this person or organisation from other sources to check if they are who they say they are
- Is this a promoted or paid piece of content? At times promoted ads at the bottom of reputable sites can be used to spread fake news. To spot them you’ll usually see an “Ad” tag next to the image or on the image. This could give you an idea around the intent behind the content. Is it trying to sell you something, or push a particular point of view?
- Does it promote a particular viewpoint? Sometimes it can be easier to believe something if we agree with the beliefs that are promoted in the content so it’s important to not take things at face value even if we agree with them
- Does it make you feel something (angry, happy, sad?) Fake news is often written to trigger an emotional response in people because that makes them more likely to engage with or share it
- Can you find it on a reputable site? Try and look around to find other trusted sources that have written about it to see if it checks out when compared side by side
- Are there any typos or other errors in the content? You will often find fake news sites will contain a lot of typos and grammatical errors on the site and URL
- Check the date – Some stories are not completely fake but are a more distorted version of real events so checking the date can help you determine if what is being said is real or fake
Wait
- Explain to your child that if anything appears too good to be true, it probably is. Or, if they still feel worried after fact-checking a source, it’s best not to share it
- Instead, give it a couple of days to see what other people think, and if you still like the story then consider sharing it
Improving children’s media literacy
Encouraging children to question the information they see online develops their critical thinking skills. When a child can think critically about a piece of information — who and where it comes from, what it’s purpose is, etc. — they can better deal with content online.
Media literacy is not just reading content online, but assessing it before sharing and discussing content with others.
Help children develop their media literacy with Digital Matters.
Have regular check-ins with children
Talking to your child about what they do and see online can help them reflect on their experiences. You can also work together by highlighting examples of mis or disinformation and discussing them.
If you’re stuck on where to start the conversation, remember that simple things can help, like discussing the difference between fact and opinion.
For younger children, you can talk about how information online is made and why. Explain that all things online have a reason behind them. The reason could be to share information or spread awareness. However, those reasons might also be making money, misleading people or becoming famous.
With older children, it’s important to stress that we tend to trust things that we agree with more than those we don’t. This is called bias. Even if they read something online that they don’t agree with, it’s important to take a step back and consider both sides.
Featured misinformation articles
 Research
Research
Connected and conflicted: Children’s perspectives on restricting social media for under-16s
We take a deep dive into children's perspectives on banning social media for under-16s to support wellbeing.
 Q&A
Q&A
How can parents manage the impacts of international news on children and teens?
Experts share advice to help parents and carers manage children's anxiety around international news.
 Expert opinion
Expert opinion
How to counter online hate and extremism with young people
Hate and Extremism Analyst, Hannah Rose, shares insight into how young people might get involved online. Learn how to counter online hate.
 News & blogs
News & blogs
What are algorithms? How to prevent echo chambers and keep children safe online
Algorithms are an important part of social media feeds, but they can create echo chambers which lead to issues of online hate, misinformation and more.
 Q&A
Q&A
Thinking critically about news on social media
Encourage children and young people to think critically about news they see on social media with expert advice from Dr. Elizabeth Milovidov and Lauren Seager-Smith.



